WANG Liyong, a doctoral candidate of CALM (first author), Professor WU Yongling and Professor ZHENG Hongyu (corresponding authors), published a paper entitled “Enhancement of antibacterial function by incorporation of silver-doped ZnO nanocrystals onto a laser-induced graphene surface” in RSC Advances.
This paper presents a method for inducing porous graphene on watercolour paper using a nanosecond laser. The high density of energy at the laser focus vaporises the paper, therefore, an out-of-focus method is used. The surface of the watercolour paper is transformed into porous graphene due to carbonisation by a simple laser scan, but the original graphene has weak bacterial inhibition, therefore, before laser induction, silver-doped zinc oxide particles are used to coat the The silver-doped zinc oxide particles were coated on the surface prior to laser induction to firmly adhere the particles to the porous graphene while inducing graphene. Bacterial inhibition experiments showed that the addition of silver-doped zinc oxide reduced the viability of graphene by 84% for S. aureus and 100% for E. coli.
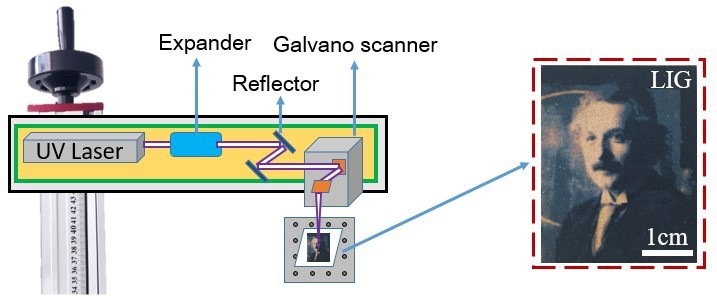
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of laser-induced graphene.
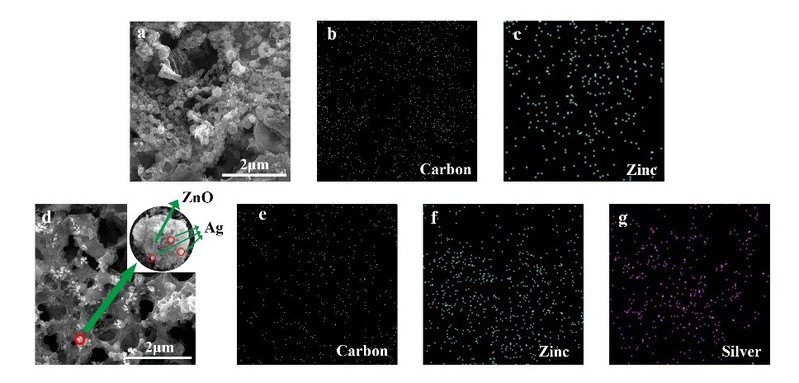
Fig. 2 (a) SEM image of LIG with ZnO. The EDS mapping of (b) carbon, (c) zinc on LIG with ZnO. (d) SEM image of LIG with Ag doped ZnO. The EDS mapping of (e) carbon, (f) zinc and (g) silver of LIG with Ag doped ZnO.
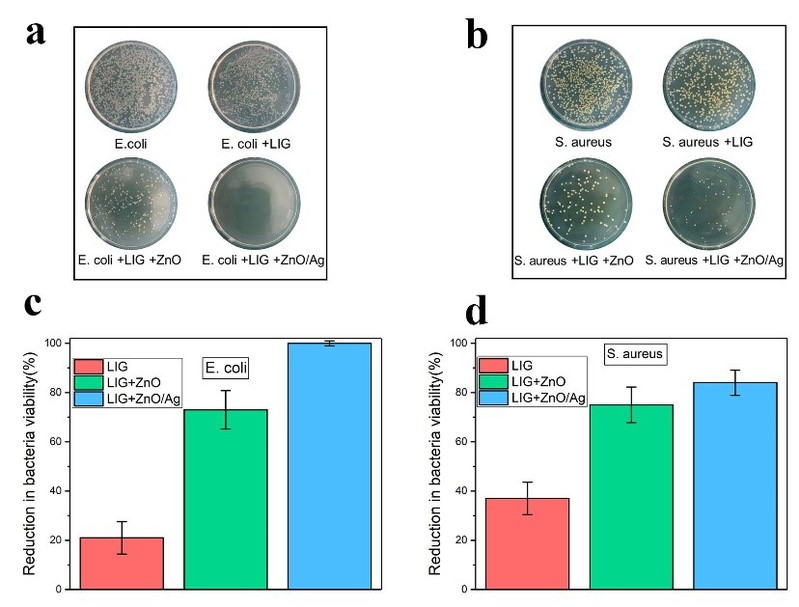
Fig. 3 Growth of (a) E. coli and (b) S. aureus colonies in different samples. Reduction in bacteria viability of (c) E. coli and (d) S. aureus in different samples.
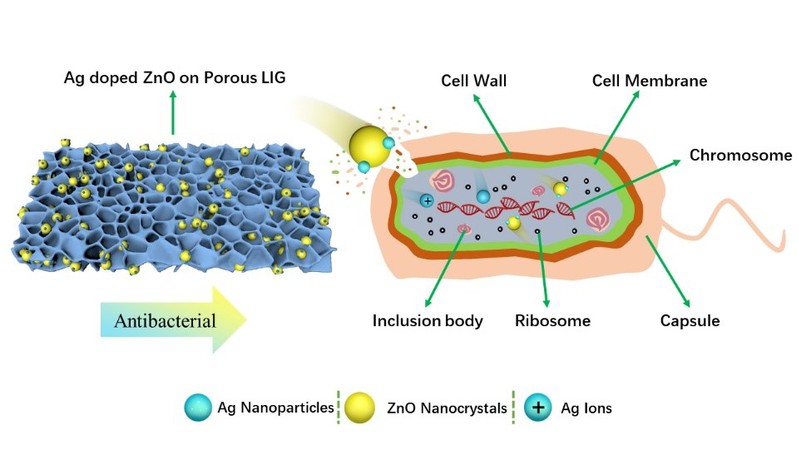
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of antibacterial mechanism of Ag doped ZnO nanocrystals.


